Professionals dealing with digital contract signing are familiar with eSignatures. But did you know that eSignatures have many different types?
Electronic signatures have revolutionized how businesses and individuals handle documents, offering convenience, efficiency, and enhanced security in digital transactions. However, understanding the nuances between the different types of electronic signatures—Qualified Electronic Signatures (QES), Advanced Electronic Signatures (AES), and Simple Electronic Signatures (SES)—is essential to ensure legal compliance and the best use of this technology.
This blog delves into the meaning, significance, and applications of each signature type, equipping you with the knowledge to choose the right option for your needs.
Introduction to Electronic Signatures
An electronic signature is a digital representation of a person's consent or agreement to the terms outlined in a document. Electronic signatures have become a cornerstone of modern business practices with the increasing digitization of workflows.
Electronic signatures streamline processes while ensuring security and compliance, whether it's closing deals, signing contracts, or authorizing financial transactions.
Importance of Electronic Signatures:
- Convenience: No need for physical presence or paper-based workflows.
- Security: Encrypted formats ensure authenticity and protect against forgery.
- Legality: Many jurisdictions recognize electronic signatures as legally binding, provided they meet specific requirements.
Electronic signatures come in various types, each with its own level of security, usability, and legal validity.
Let’s explore the three main types of electronic signatures: Qualified Electronic Signatures (QES), Advanced Electronic Signatures (AES), and Simple Electronic Signatures (SES).
Understanding Qualified Electronic Signatures (QES)
The Qualified Electronic Signature (QES) is the most robust and legally binding type of electronic signature. Defined under the eIDAS (Electronic Identification, Authentication, and Trust Services) regulation in the EU, a QES is the digital equivalent of a handwritten signature.
QES Meaning and Features:
- Legal Validity: A QES holds the same legal standing as a handwritten signature, making it suitable for highly regulated transactions.
- Certification: It is based on a qualified certificate from a trusted QES signature provider.
- Verification: The signer's identity is rigorously verified to ensure authenticity.
Common Use Cases:
- Signing legal agreements such as wills, deeds, and contracts.
- Authorization of high-value financial transactions.
- Regulatory compliance in healthcare and banking sectors.
Understanding Simple Electronic Signatures (SES)
A Simple Electronic Signature (SES) is the most basic form of digital signature. It includes any form of electronic data (e.g., scanned images of handwritten signatures or typed names) that signifies consent.
Features of SES:
- Flexibility: Easy to create and use for informal or low-risk transactions.
- Limited Security: Lacks encryption and other advanced features.
- Legal Standing: This may not be legally binding in all jurisdictions.
Common Use Cases:
- Daily transactions like delivery confirmations.
- Signing consent forms or non-disclosure agreements.
- Informal business approvals.
While SES is easy to implement, its lack of robust security features makes it unsuitable for sensitive documents.
Understanding Advanced Electronic Signatures (AES)
An Advanced Electronic Signature (AES) provides a higher level of security than SES while maintaining ease of use. It is unique to the signer and linked to the data being signed, ensuring integrity and authenticity.
Features of AES:
- Enhanced Security: Incorporates cryptographic techniques to detect tampering.
- AES Certification: Requires the signer to possess a digital certificate.
- Jurisdiction-Specific Validity: While not as universally accepted as QES, it is legally binding in many regions.
Common Use Cases:
- Signing corporate documents.
- Approving employee contracts.
- Validating sensitive business communications.
AES strikes a balance between usability and security, making it ideal for mid-level transactional needs.
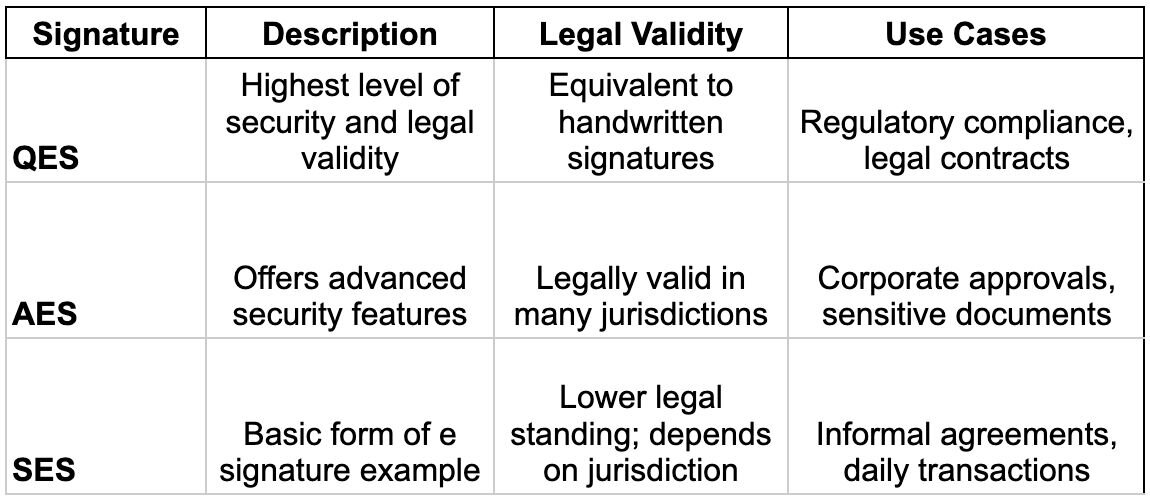
Types of Electronic Signatures: A Comparative Overview
Here’s a quick comparison of Qualified Electronic Signatures (QES), Advanced Electronic Signatures (AES), and Simple Electronic Signatures (SES):
Each type of electronic signature caters to different security needs and legal requirements, offering flexibility in document management.
How to Obtain a Qualified Electronic Signature
Obtaining a Qualified Electronic Signature (QES) involves a structured process to ensure security and compliance:
Steps to Obtain a QES:
- Choose a Trusted Provider: Select a certified QES signature provider that meets your region’s legal standards.
- Verify Your Identity: Undergo a thorough identity verification process, often involving official ID documents or in-person verification.
- Obtain a Digital Certificate: This certificate forms the backbone of your QES, linking your identity to your electronic signature.
- Start Signing Documents: Use the provider’s platform to securely sign documents with your QES.
An e signature example using a QES might include signing a business merger agreement digitally, ensuring both parties' identities are verified.
Security Aspects of Qualified Electronic Signatures
Security is a cornerstone of electronic signatures, with QES offering the highest protection against fraud.
How QES Ensures Security:
- Encryption: Ensures the signed document cannot be altered without detection.
- Authentication: Verifies the signer's identity via trusted certification authorities.
- Non-Repudiation: Prevents signers from denying their signatures.
While SES security is minimal, AES provides an intermediate level of protection with cryptographic checks.
Legal Requirements for Using QES, AES, and SES
To ensure your electronic signatures are legally binding, it’s crucial to comply with regional regulations such as:
- eIDAS (EU): Governs QES, AES, and SES in the European Union.
- ESIGN Act (USA): Recognizes all types of electronic signatures as legally valid.
- IT Act (India): Endorses digital signatures with a focus on secure certificates.
Use Cases for Qualified Electronic Signatures
Common Use Cases for QES:
- Legal Documents: Signing contracts, deeds, or affidavits.
- Financial Agreements: Approving loans or investment deals.
- Corporate Contracts: Ensuring secure, high-stakes business transactions.
For example, in the legal field, QES provides a unique signature format that ensures compliance and prevents tampering.
FAQs about QES:
1. What is the difference between QES and AES?
Qualified Electronic Signatures (QES) and Advanced Electronic Signatures (AES) both offer high levels of security but differ in their legal standing and requirements.
- QES provides the highest level of security and legal validity. It is certified by a qualified trust service provider, with stringent identity verification processes. In legal terms, a QES is considered equivalent to a handwritten signature and is recognized across many jurisdictions under regulations like eIDAS.
- AES, while secure and capable of detecting tampering, offers a slightly lower level of assurance than QES. It uses cryptographic methods to ensure authenticity but does not require the same level of identity verification or certification.
For high-stakes documents like legal contracts or financial agreements, a QES signature is ideal. For less critical use cases like internal approvals, an AES signature may suffice.
2. How legally binding is a QES?
A Qualified Electronic Signature (QES) is legally binding and is considered equivalent to a handwritten signature in most jurisdictions, including the EU (under eIDAS) and other regions that recognize similar certifications. This legal equivalence ensures that documents signed with a QES can be upheld in court if necessary.
Read Here: Difference Between Electronic and Digital Signature
By contrast, while AES and SES may be accepted in some situations, their legal standing often depends on the context and jurisdiction. A QES provides unmatched assurance that the signer’s identity and intent are fully authenticated, making it the preferred choice for unique signature needs in highly regulated industries like finance, law, and healthcare.
3. Can I use QES internationally?
Yes, a Qualified Electronic Signature can be used internationally, but compliance depends on the regulations of the recipient's country. For example:
- In the EU, QES is universally recognized under the eIDAS regulation, ensuring cross-border compatibility.
- Outside the EU, countries like the USA (under the ESIGN Act) and India (under the IT Act) recognize electronic signatures, but additional verification may be required.
When using a QES internationally, ensure that the recipient country accepts the electronic signature format and the certification authority issuing the QES. Platforms like ZoopSign provide QES signature providers that comply with global standards, making it easier to manage cross-border transactions securely.
4. What are the costs of obtaining a QES?
The cost of obtaining a Qualified Electronic Signature (QES) varies based on factors such as:
- Provider Fees: Different QES signature providers charge varying fees for issuing and maintaining digital certificates.
- Identity Verification: Some providers may charge additional fees for in-person or advanced identity verification processes.
- Subscription Plans: Many platforms, including ZoopSign, offer flexible pricing models, such as pay-per-use or annual subscriptions.
Investing in a QES might seem costly initially, but its ability to ensure compliance, mitigate risks, and simplify documentation in critical transactions makes it a worthwhile expenditure for businesses and professionals.
5. Do I need special software for QES?
No, you don’t need complex software to use a QES. Most trusted providers offer user-friendly platforms with intuitive interfaces to simplify the signing process. For instance:
Providers like ZoopSign offer a web-based solution or app-based solution that integrates seamlessly with your document management system. These platforms handle everything—from document uploading to verification, applying the QES, and securely storing the signed files. Some providers also support integrations with commonly used tools like Microsoft Office, Google Workspace, or CRM systems, enhancing usability.
The key is to choose a provider that offers a certified QES signature format while ensuring ease of use, making it practical for day-to-day business needs.
Why Choose the Right Electronic Signature Type?
Selecting the appropriate type of electronic signature—whether QES, AES, or SES—is more than a legal necessity; it’s a strategic decision for businesses and individuals aiming to streamline operations while maintaining security and compliance. Each type of signature serves a unique purpose, catering to different levels of security, ease of use, and legal validity. By understanding these distinctions, you can confidently choose the best solution for your specific needs.
Why ZoopSign is Your Trusted Partner for E Signatures
At ZoopSign, we understand the importance of providing secure, user-friendly, and legally compliant electronic short signature solutions. Whether you’re looking for the uncompromising security of QES, the enhanced flexibility of AES, or the simplicity of SES, ZoopSign has you covered.
Why ZoopSign Stands Out:
- Comprehensive Signature Options: From simple signatures to qualified electronic signatures, our platform offers every type of electronic signature tailored to your business needs.
- Seamless Integration: ZoopSign integrates effortlessly into your existing workflows, ensuring a smooth and intuitive signing experience.
- Global Compliance: We adhere to international standards like eIDAS, ESIGN, and IT Act, ensuring your documents are legally recognized worldwide.
- Top-Tier Security: With industry-leading AES certifications and compliance protocols, ZoopSign guarantees that your documents are protected against fraud and unauthorized access.
- Exceptional Support: Our team is here to guide you, from choosing the right QES signature provider to implementing advanced security measures.
Whether you're a freelancer, small business owner, or part of an enterprise, ZoopSign empowers you to handle all your electronic signature letters needs confidently. Experience the future of secure, hassle-free digital transactions with ZoopSign.